Yarn Abrasion and Friction Testing
TTI testing now has it's own website:
TTI Testing (Rope, chain, cable and yarn testing)We design tests to help manufacturers and users quantify the performance of a rope or cable.
Our forensic service helps establish the root cause of accidents and failures.Tension Technology Incorporated (TTI) engineers have much experience in developing, performing, and analysing tests for yarn tensile properties, yarn-on-yarn and yarn-external abrasion performance and yarn-on-yarn coefficient of friction.
We have the most extensive independently measured database of material properties as follows
- Break load
- Break extension
- Friction
- Abrasion Life
- Creep strain
- Axial compression
On the following materials
- Polyester
- Nylon
- Kevlar
- Twaron
- Technora
- Dyneema
- Spectra
- PBO
- PEN
- Vectran
Yarn Tensile Properties
Yarn tensile strength and elongation are the primary properties that, along with construction, determine a rope’s strength and stiffness. With repeated loading, yarns tend to stiffen and this is reflected in the yarn dynamic modulus. After a period of relaxation, the yarn will recover and the modulus falls to a value close to the original modulus value.
Creep and Stress Rupture are also important properties to characterise. After initial yarn loading, creep tends to reduce; following a logarithmic relationship. As failure approaches, creep accelerates and finally stress rupture occurs
Yarn-on-Yarn Friction
The coefficient of friction of rope making yarns has a major influence on rope strength. A low coefficient of friction allows yarns and strands to realign under load, thus redistributing stresses and increasing rope strength. A high coefficient of friction contributes to the strength and durability of splices. Very high or very low friction can accordingly reduce rope strength.
For yarn friction measurements we perform an adaptation of the ASTM "Standard Test Method for Coefficient of Friction, Yarn to Yarn". We employ a special test machine and test at a number of different applied tensions. We can perform this test at different yarn speeds. We can also adapt this machine to measure coefficient of friction of yarn on various other materials.
We have performed such friction tests on many different rope-making yarns; nylon, polyester, aramid, HMPE, etc.
Yarn-on-Yarn Abrasion
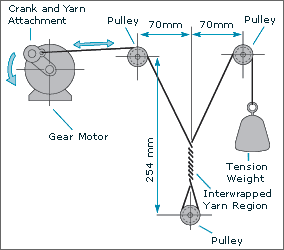
Yarn-on-Yarn abrasion setupInternal abrasion between fibres, yarns, and strands is one of the principal causes of rope degradation, especially in cyclic tension or bend-over-sheave service. TTI personnel have developed special testing techniques and performed extensive testing for rope-making yarn abrasion resistance.
The basic test machine and technique was developed by Dr. Hearle and John Flory, both now of TTI, together with a graduate student, at the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology. That work was performed under sponsorship of a group of oil companies interested in improving the quality of large hawsers. Further enhancements have now been made to the test machine design and testing technique.
We have published a number of papers on the technique. The method does not yet appear in any published national or international test standard. However, several fibre producers and rope manufacturers now have yarn abrasion test machines and use the methods for yarn evaluation and quality assurance.
In recent years we have performed such yarn abrasion tests on many rope-making yarns for various clients. Several fibre manufacturers have used results of these tests to determine the potential of new yarn products and to develop appropriate finishes for rope making. For example, Hoechst Celanese tested both Vectran LCAP and a new polyester yarn product by these abrasion resistance techniques.Yarn External Abrasion
External abrasion resistance is important in many rope applications. Concentrated damage due to rubbing against fittings and distributed damage due to dragging on deck or the ocean floor can both cause significant strength loss. Wet abrasion resistance can be substantially different from dry abrasion resistance.
We have developed methods for comparing the external abrasion performance of rope making yarns. This employees an adaptation of the yarn-on-yarn abrasion test machine and technique. Various grades of silicon carbide paper or a replaceable stainless steel screen can be used as the abradant. Thus the external abrasion testing can be performed on either wet or dry yarns.
Interpretation and Use of Yarn Property Data
All of these yarn and rope property testing techniques provide relative comparative test results. They provide general indications of rope performance, but they can not be used directly to predict rope strength or useful life. Accordingly, it is usually necessary to perform comparative tests between the new yarn product and other yarns for which rope properties are well known.
We have the experience to interpret the test data and make recommendations. We can employ our rope design computer programs to make predictions of rope performance, especially when comparative yarn friction or abrasion data is achieved for a yarn with known rope-making properties.
TTI can perform yarn-on-yarn and yarn-external abrasion tests and yarn-on-yarn friction tests on samples of yarns in our laboratories. We can also manufacture test machines and provide on-site training so that you can use the techniques in your laboratory for product development and quality assurance.
Marine Abrasion & Friction Testing
您位于服务页面

